Table of Contents
- What is ScaleDP?
- How to Use ScaleDP for Efficient Structured Data Extraction from PDFs
- 1. Define Your Data Schema for Document Processing
- 2. Create the Spark Pipeline for AI-Powered Data Extraction
- 3. Process Your PDFs with ScaleDP and Spark-PDF
- 4. View Your Structured Data in Spark DataFrames or JSON Format
- Conclusion
- Links
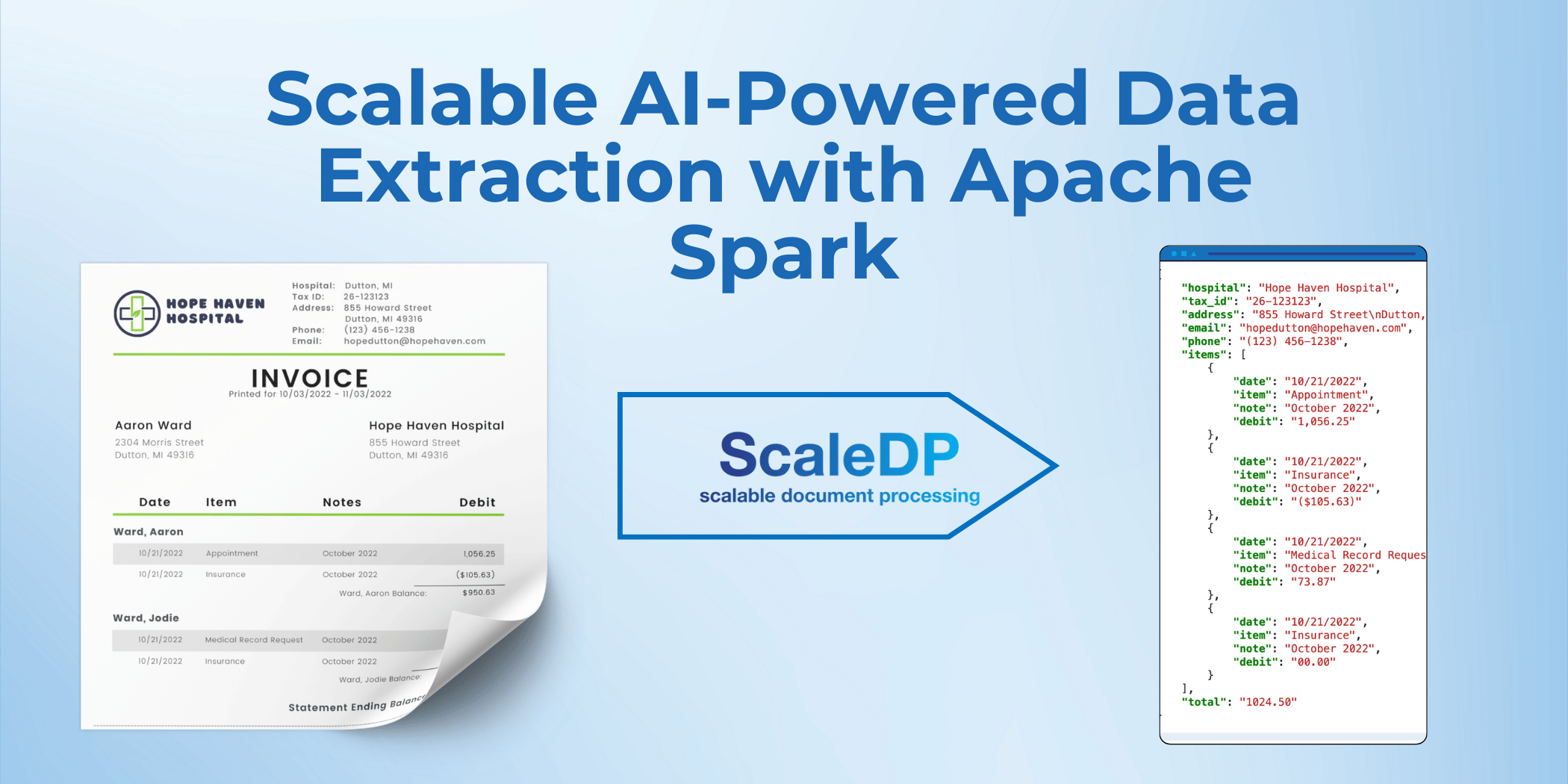
Structured Data Extraction from PDFs with AI
Machine Learning & Data Processing Expert
Data / ML Engineer
In this post, we’ll show you how ScaleDP can elevate your Spark-PDF workflow by making document processing smarter and faster. We’ll specifically focus on how to get started with structured data extraction, which can save you hours of manual work.
What is ScaleDP?
ScaleDP is an open-source library allows you to process documents using AI/ML capabilities and scale it using Apache Spark.
More Links:
- ScaleDP GitHub Repository
- ScaleDP Tutorials GitHub Repository
- ScaleDP QuickStart Colab Notebook
- ScaleDP with Spark-PDF Notebook
How to Use ScaleDP for Efficient Structured Data Extraction from PDFs
While Spark-PDF reads PDFs into Spark DataFrames, it doesn't extract structured data. ScaleDP solves this by using pre-trained AI models to automatically extract key information from documents like invoices, contracts, or forms, freeing you to focus on higher-level tasks.
Using ScaleDP with Spark-PDF simplifies the process of extracting structured data from PDFs. Here’s how to get started:
1. Define Your Data Schema for Document Processing
The first step is to define the schema for the data you want to extract from the PDF. For example, if you’re processing invoices, your schema might include fields like hospital name, tax ID, items, and the total amount.
Here's an example of how you can define your schema for an invoice:
class Items(BaseModel):
date: str
item: str
note: str
debit: str
class InvoiceSchema(BaseModel):
hospital: str
tax_id: str
address: str
email: str
phone: str
items: list[Items]
total: str
Defining this structure allows ScaleDP's AI models to automatically identify the relevant fields in your document and extract the data accordingly.
2. Create the Spark Pipeline for AI-Powered Data Extraction
Next, set up the Spark pipeline to process the document using AI models. This pipeline defines how to extract data from the PDF and map it to the schema you've defined.
pipeline = PipelineModel(stages=[
LLMVisualExtractor(
model="gemini-1.5-flash",
apiKey="your_key",
apiBase="https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/",
schema=InvoiceSchema,
outputCol="invoice"
)
])
To connect to an AI model provider like Gemini or OpenAI, ensure that you have the correct API key and base URL. Once the connection is made, the pipeline will automatically extract the data from your PDFs.
3. Process Your PDFs with ScaleDP and Spark-PDF
Once your pipeline is set up, you can process your document through ScaleDP to extract the data:
result = pipeline.transform(df).cache()
ScaleDP uses zero-shot AI models, which means you don’t have to manually tag or label data. Define the schema, and the AI will do the rest.
4. View Your Structured Data in Spark DataFrames or JSON Format
One of the key benefits of ScaleDP is how quickly and easily you can get started. Thanks to the zero-shot nature of the AI models, there's no need to spend time labeling or tagging data manually. Simply define your data structure, and let the AI handle the extraction and structuring.
Once the document is processed, the extracted data will be displayed in a structured format, such as a Spark DataFrame or JSON, for easy analysis or integration with other systems.
Here’s an example of how the data might appear in a DataFrame:
result.select("invoice.data.*").show()
The output might look like this:
| hospital | tax_id | address | phone | items | total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hope Haven Hospital | 26-123123 | 855 Howard Stree... | hopedutton@hopeha... | (123) 456-1238 | [{10/21/2022, App... | 1024.50 |
Alternatively, you can display the data in JSON format:
result.show_json("invoice")
This will provide structured, easy-to-read data ready for further analysis:
{
"hospital": "Hope Haven Hospital",
"tax_id": "26-123123",
"address": "855 Howard Street\nDutton, MI 49316",
"email": "hopedutton@hopehaven.com",
"phone": "(123) 456-1238",
"items": [
{
"date": "10/21/2022",
"item": "Appointment",
"note": "October 2022",
"debit": "1,056.25"
},
{
"date": "10/21/2022",
"item": "Insurance",
"note": "October 2022",
"debit": "($105.63)"
},
{
"date": "10/21/2022",
"item": "Medical Record Request",
"note": "October 2022",
"debit": "73.87"
},
{
"date": "10/21/2022",
"item": "Insurance",
"note": "October 2022",
"debit": "00.00"
}
],
"total": "1024.50"
}
Conclusion
Using ScaleDP and Spark-PDF together allows you to effortlessly extract structured data from PDFs. The key steps include defining your data schema, setting up the Spark pipeline, processing the document, and viewing the extracted data. This process is fast, accurate, and doesn't require manual data tagging, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Because ScaleDP is built on top of Apache Spark, it’s also great for processing large datasets. Whether you’re dealing with hundreds or thousands of PDFs, ScaleDP can process them in parallel, making your workflow faster and more efficient.
Links
Project Details:
GitHub Repositories:
Colab Jupyter Notebooks with Usage Samples: